Redefining Dental Age Estimation: From Eruption Charts to Digital Precision
Introduction
Dental age estimation is one of the most accurate and reliable tools in forensic science. It plays a critical role in both human identification and broader legal and humanitarian contexts. Forensic odontologists use dental development stages and structural changes in teeth to estimate age in both the living and the deceased. This supports a wide range of investigations, from anthropology and archaeology to disaster victim identification and court cases involving undocumented individuals or age disputes.
Why Teeth Are Ideal for Age Estimation
Tooth development begins before birth and continues into early adulthood, making teeth a dependable biological marker of chronological age. Unlike skeletal or sexual maturity indicators, dental formation is less affected by nutrition, environment, or hormonal changes, ensuring more consistency across populations.
Traditional approaches focused mainly on eruption patterns, but conditions like ankylosis, impaction, or early extractions can disrupt these sequences. As a result, modern methods now prioritize tooth development stages and degenerative dental changes, assessed both visually and radiographically, to offer more objective and accurate age estimations.
Traditional approaches focused mainly on eruption patterns, but conditions like ankylosis, impaction, or early extractions can disrupt these sequences. As a result, modern methods now prioritize tooth development stages and degenerative dental changes, assessed both visually and radiographically, to offer more objective and accurate age estimations.
Age Group Categories and Methods
Age estimation techniques focus on tooth development under 22 and structural changes after 22.
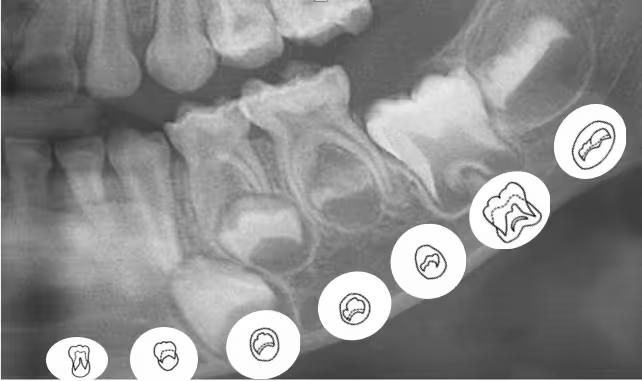
- Under 22 Years – Development-Based Methods
1. Children (Birth to 5 years): Focuses on the eruption and formation of primary (baby) teeth.
2. Juveniles (6 to 14 years): Uses dental scores of developing permanent teeth (excluding third molars).
3. Adolescents (15 to 21 years): Evaluates third molar (wisdom tooth) development, particularly useful in legal age assessments.
- 22+ Years – Degeneration-Based Methods
1. Radiographic Tooth Analysis: Assesses pulp-to-tooth ratio using X-rays; non-invasive and widely adopted.
2. Intact Tooth Analysis: Measures root transparency and gum attachment in whole, extracted teeth.
3. Sectioned Tooth Analysis: Involves slicing teeth to examine internal features like secondary dentin or cementum layering.
Age Group Categories and Methods
When conventional assessments are not feasible, biochemical and imaging methods offer precise alternatives:
- Carbon-14 Dating: Reflects birth year by measuring radiocarbon levels in dental enamel.
- Aspartic Acid Racemization: Estimates age at death by analyzing protein breakdown in dentin.
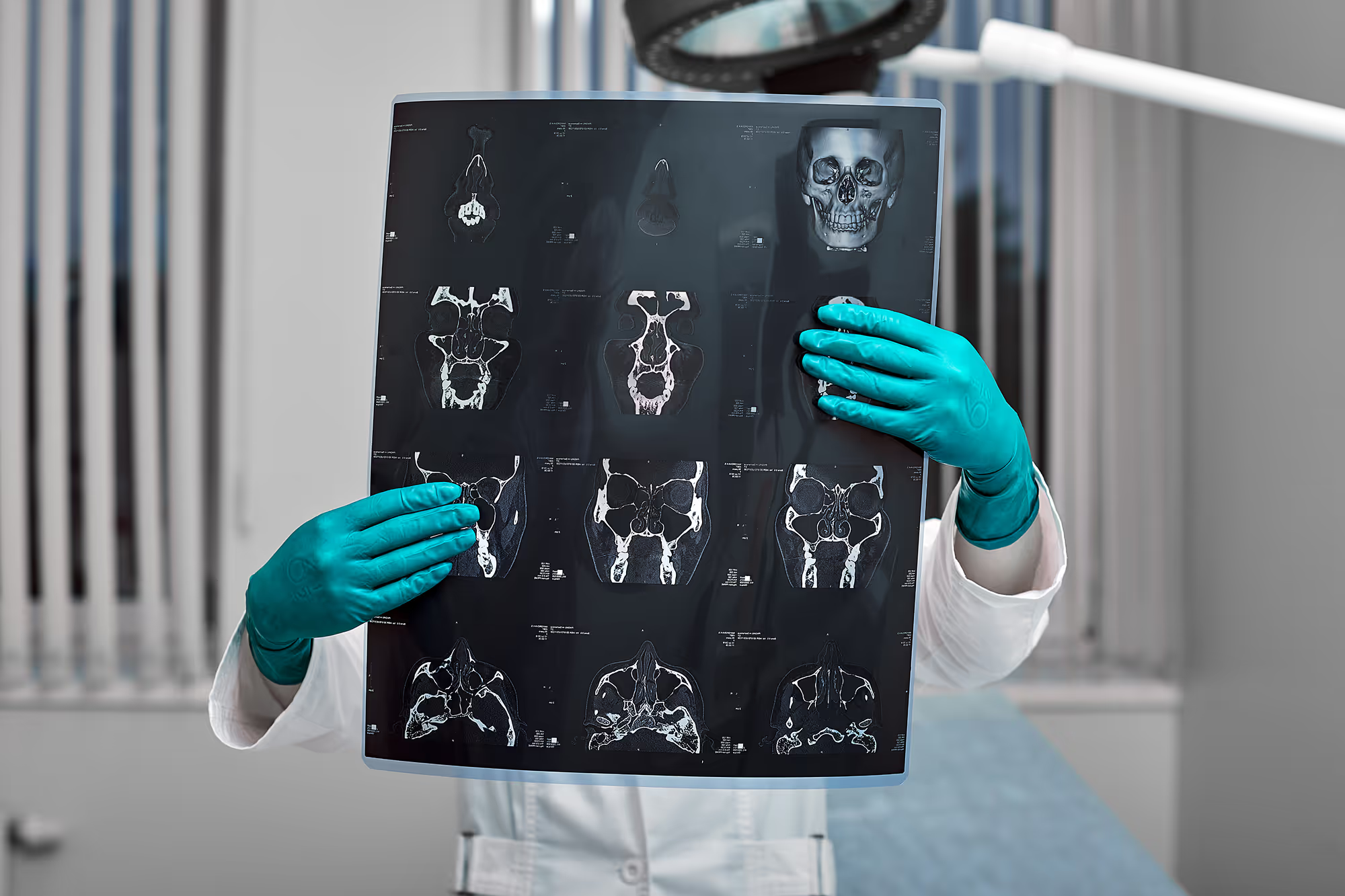
- Cone Beam CT (CBCT): offers 3D imaging to calculate tooth-to-pulp ratios for age estimation.
- Orthopantomograph (OPG) & Periapical Radiographs:
1. OPGs capture panoramic jaw images to assess overall development.
2. Periapical shows individual teeth for assessing pulp size, root growth, and closure.
Advancing Age Estimation with Dental ID
Dental ID represents a breakthrough in modern age estimation. This innovative software integrates digital radiography, standardized staging systems, and AI-assisted evaluation into a single, streamlined platform.
It intelligently selects the appropriate method based on age group and data type, structures radiographic inputs such as tooth development stages or pulp-to-tooth ratios, and generates standardized, evidence-based reports.
Dental ID reduces subjectivity and ensures consistent, evidence-based assessments, advancing age estimation in legal, humanitarian, and disaster scenarios with speed and precision.
It intelligently selects the appropriate method based on age group and data type, structures radiographic inputs such as tooth development stages or pulp-to-tooth ratios, and generates standardized, evidence-based reports.
Dental ID reduces subjectivity and ensures consistent, evidence-based assessments, advancing age estimation in legal, humanitarian, and disaster scenarios with speed and precision.